DMAIC is a cyclical process, and once a project is completed, the team can start the DMAIC cycle over again to tackle another process improvement opportunity. This iterative approach ensures that an organization continually works on enhancing its processes and maintaining a focus on quality and efficiency. DMAIC is a core component of Lean Six Sigma and provides a systematic and data-driven framework for achieving process improvements and problem-solving.
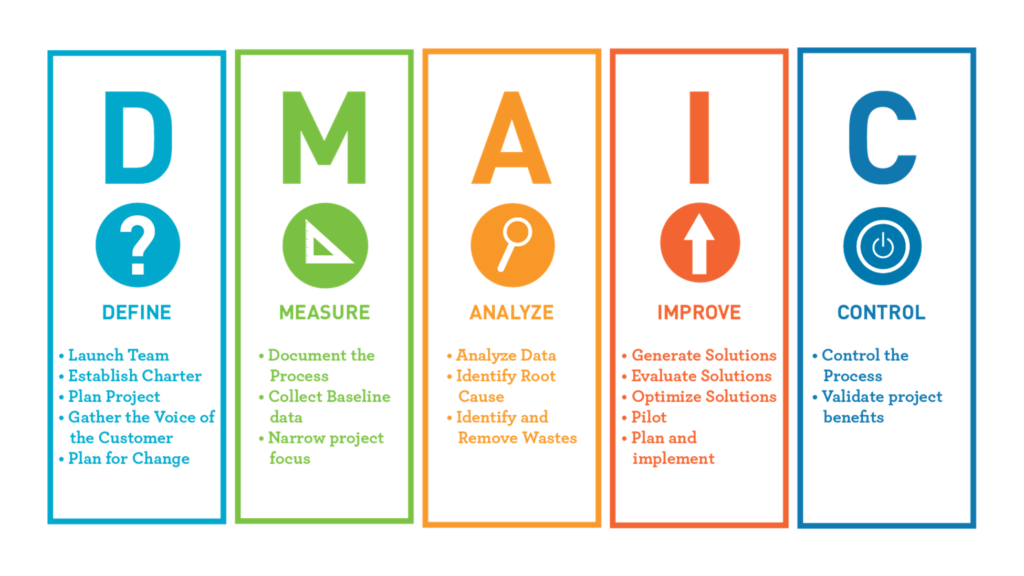
DMAIC is a structured problem-solving and process improvement methodology used in Lean Six Sigma. The acronym DMAIC stands for:
- Define: In this initial phase, the project team defines the problem or opportunity for improvement, sets project goals, and identifies the critical elements of the process that need improvement. This stage involves creating a project charter that outlines the scope, objectives, and resources required for the project.
- Measure: During the Measure phase, the team collects data and quantifies the existing process’s performance. This step involves defining key performance metrics (KPIs) and developing a data collection plan to ensure accurate measurement.
- Analyze: In the Analyze phase, the team analyzes the data collected in the Measure phase to identify the root causes of problems or variations in the process. Various statistical and analytical tools are employed to uncover the underlying issues affecting process performance. The goal is to pinpoint the specific areas that need improvement.
- Improve: The Improve phase focuses on developing and implementing solutions to address the identified root causes. The team generates, tests, and refines potential solutions to optimize the process. These solutions are typically designed to reduce defects, errors, waste, or other issues that were identified during the Analyze phase.
- Control: The Control phase involves implementing controls and measures to ensure that the improvements made in the previous phases are sustained over time. It includes setting up monitoring systems, standardizing processes, and establishing procedures to prevent the recurrence of problems. This phase aims to lock in the gains achieved through the project.
