What are the types of Data?
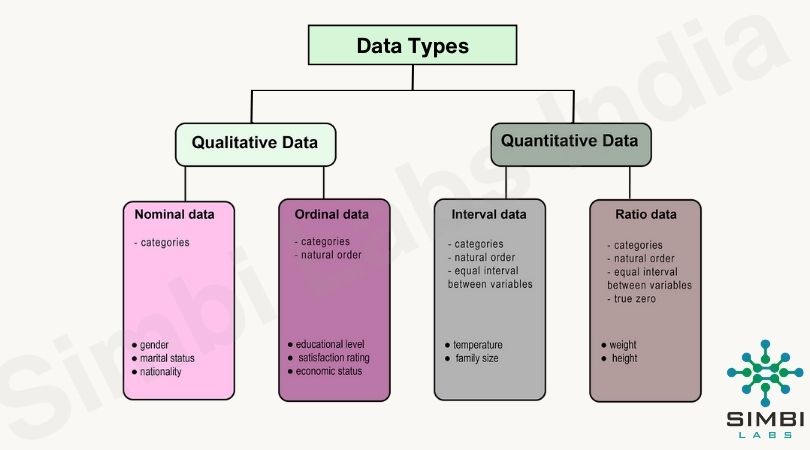

There are two main types of data: qualitative (categorical) and quantitative (numerical). Within these broad categories, there are subtypes that provide more specific information about the nature of the data.
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that combines Lean (focused on reducing waste) and Six Sigma (focused on reducing variation and improving quality). There are different types of Lean Six Sigma approaches based on their applications and objectives. Here are the main types:
1. DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control)
2. DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify) / DFSS (Design for Six Sigma)
3. Lean Six Sigma in Manufacturing
4. Lean Six Sigma in Services
5. Lean Six Sigma in Healthcare
6. Lean Six Sigma in Supply Chain & Logistics
7. Kaizen (Continuous Improvement)
Lean Six Sigma is driven by a combination of Lean principles (eliminating waste) and Six Sigma (reducing process variation). Here are the key factors that influence its success:
1. Customer Focus
2. Data-Driven Decision Making
3. Process Standardization & Improvement
4. Waste Reduction (Lean Principles)
5. Variation & Defect Reduction (Six Sigma Principles)
6. Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)
7. Strong Leadership & Employee Involvement
8. Effective Use of Lean Six Sigma Tools
9. Cost Reduction & Efficiency
10. Sustainable Change & Control Measures
Lean Six Sigma provides numerous benefits across industries by improving efficiency, reducing waste, and enhancing quality. Here are the key advantages:
1. Improved Quality & Reduced Defects
2. Increased Efficiency & Productivity
3. Cost Reduction
4. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
5. Data-Driven Decision Making
6. Competitive Advantage
7. Better Employee Engagement & Skill Development
8. Stronger Risk Management
9. Sustainability & Long-Term Growth
10. Cross-Industry Applicability